Nectus and Azure SAML Integration
Step 1: Navigate to Identity -> Enterprise Applications from within the Azure Portal:
Step 2: To add a new application, click the new application button:
Step 3: Create your own application:

Step 4: In the application panel, select Non-Gallery application and enter a name (for example, Nectus5) and Select Create
Step 5: Navigate to Manage-> Single Sign On found on the left-hand panel and select SAML for the SSO method:
Step 6: On the Set up Single Sign-On with SAML page, click the Edit icon to open the
Basic SAML configuration dialog:
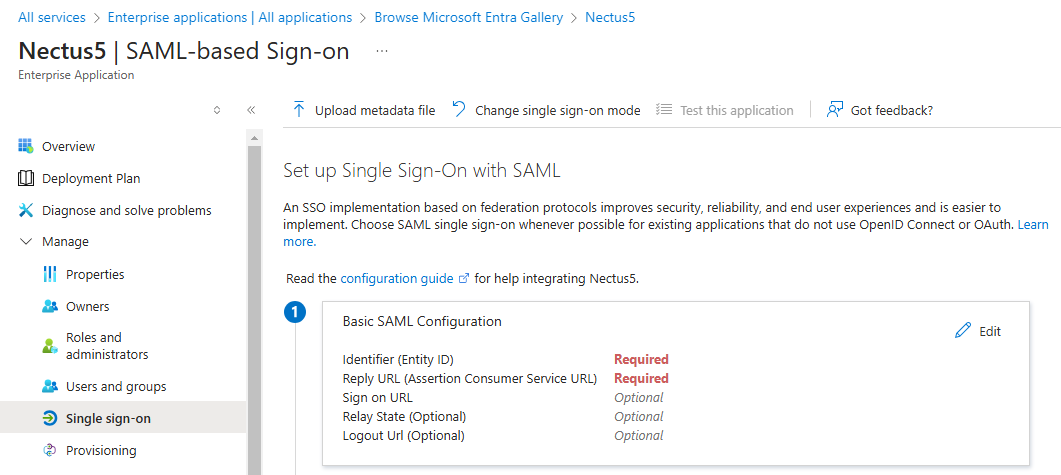
Step 7: On the Basic SAML Configuration section, perform the following steps (please note these are the default values out of the box and will be different for every organization):
- In the Identifier textbox, type the value:
https://base22c/saml
- In the Reply URL textbox, type the value:
https://base22c/saml/acs
- In the Sign-on URL textbox, type the value:
https://base22c/saml
Step 8: In the User “Attributes and Claims’ section, check that Azure is passing at least the following claims: givenname, surname, emailaddress, name, and unique User Identifier (this is the default setting)
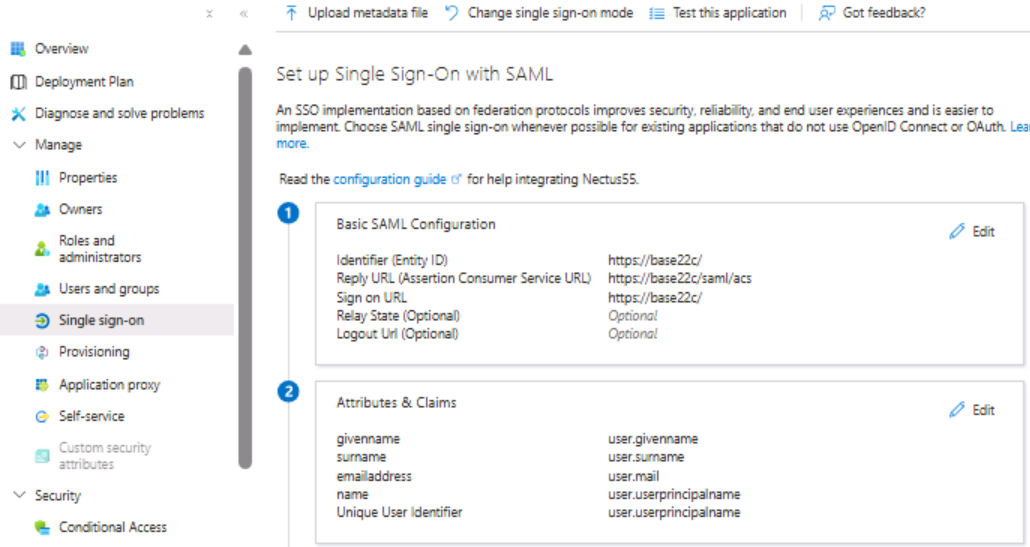
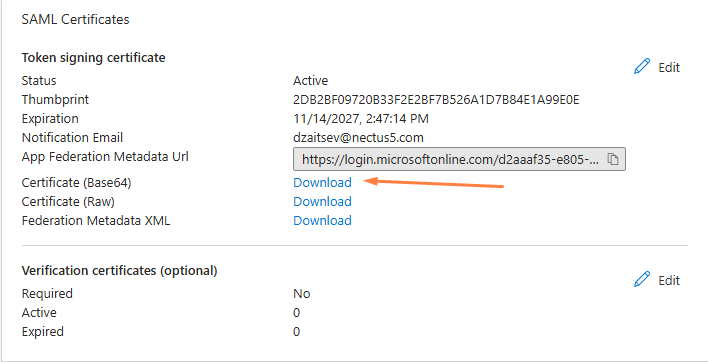
Step 9: On the “SAML Certificates” section, download the Base64 certificate and save it to your computer.
Step 10: Navigate to Nectus, and open the SAML configuration settings:
Step 11: Take the values listed for the Login URL, Azure AD Identifier, and Logout URL, and paste these to the corresponding sections in the SAML configuration settings in Nectus.
Ensure the SAML Provider selected is Azure:
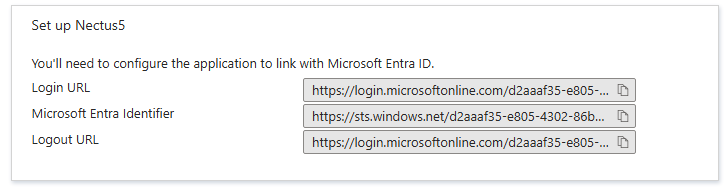
In Nectus5:
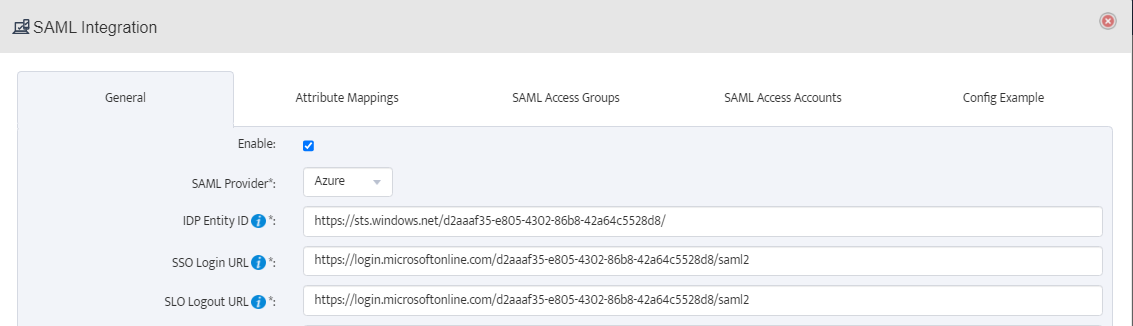
The certificate value is the plaintext value of the Base64 certificate downloaded previously (rename the file with a .txt extension and copy the string from Notepad):
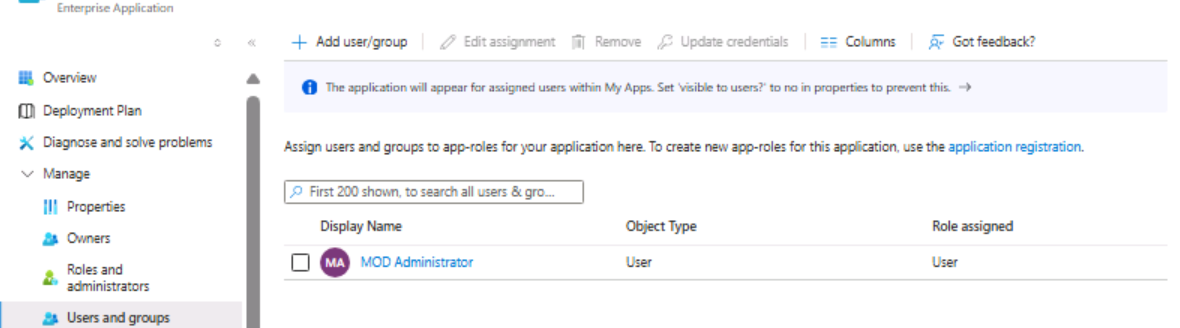
Step 12: Assign Users and Groups to the enterprise application in the Azure portal:
Step 13: Finish the remaining configuration on the Nectus5 application for Attribute Mapping, SAML access groups, and SAML access accounts:
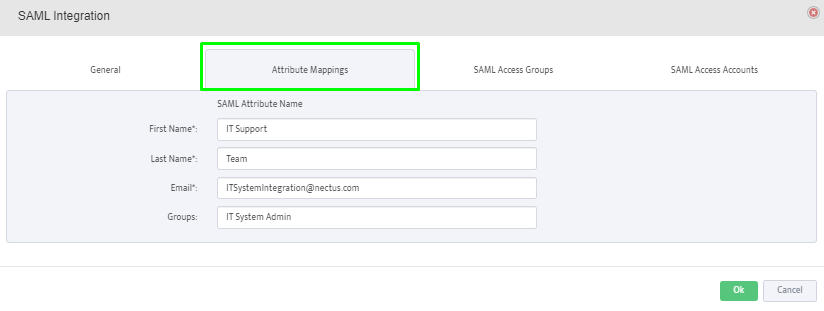
Attribute Mappings: provide the SAML attributes for First Name, Last Name, Email and membership Groups. This mapping is between SAML attributes and Nectus fields.
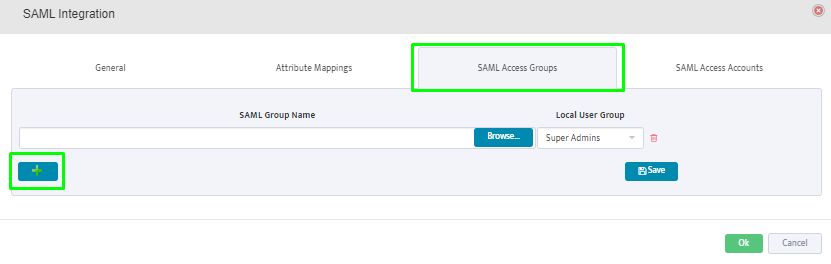
SAML Access Groups: Click on the “+” button to add the SAML user groups from the SAML Server.
Members of the selected groups will be allowed to login to Nectus.
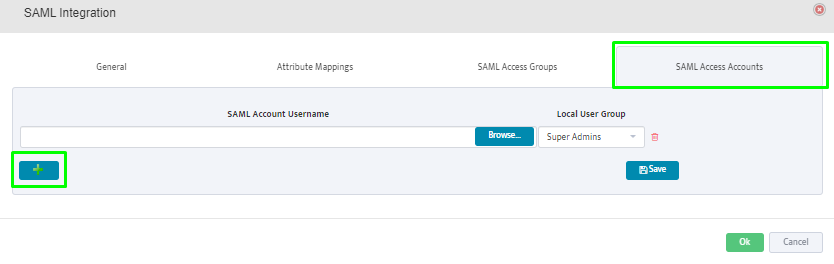
SAML Access Accounts: Click on the “+” button to add individual user accounts from the SAML Server.
Selected users will be allowed to login to Nectus.
Creating service account for MSSQL monitoring in Nectus
Access Right Management, Technical NotesCreating MS SQL DB Monitoring Service Account for Nectus
Step 1 : Connect to MS SQL Server
Step 2 : Under “Security” tab, open “Logins” section.
Step 3 : Right-click on “Logins” section , and select “New Login”.
Step 4 : Fill in the required information for the new account.
Step 5 : In “New Login” window “General” tab specify:
Step 6: For “Server Roles” select “sysadmin” and “public”.
Step 7: for “User Mapping” select the database and also select database role as “db_datareader”.
Nectus Azure SAML Integration
Nectus Installation, Technical NotesNectus and Azure SAML Integration
Step 1: Navigate to Identity -> Enterprise Applications from within the Azure Portal:
Step 2: To add a new application, click the new application button:
Step 3: Create your own application:
Step 4: In the application panel, select Non-Gallery application and enter a name (for example, Nectus5) and Select Create
Step 5: Navigate to Manage-> Single Sign On found on the left-hand panel and select SAML for the SSO method:
Step 6: On the Set up Single Sign-On with SAML page, click the Edit icon to open the
Basic SAML configuration dialog:
Step 7: On the Basic SAML Configuration section, perform the following steps (please note these are the default values out of the box and will be different for every organization):
https://base22c/saml
https://base22c/saml/acs
https://base22c/saml
Step 8: In the User “Attributes and Claims’ section, check that Azure is passing at least the following claims: givenname, surname, emailaddress, name, and unique User Identifier (this is the default setting)
Step 9: On the “SAML Certificates” section, download the Base64 certificate and save it to your computer.
Step 10: Navigate to Nectus, and open the SAML configuration settings:
Step 11: Take the values listed for the Login URL, Azure AD Identifier, and Logout URL, and paste these to the corresponding sections in the SAML configuration settings in Nectus.
Ensure the SAML Provider selected is Azure:
In Nectus5:
The certificate value is the plaintext value of the Base64 certificate downloaded previously (rename the file with a .txt extension and copy the string from Notepad):
Step 12: Assign Users and Groups to the enterprise application in the Azure portal:
Step 13: Finish the remaining configuration on the Nectus5 application for Attribute Mapping, SAML access groups, and SAML access accounts:
Attribute Mappings: provide the SAML attributes for First Name, Last Name, Email and membership Groups. This mapping is between SAML attributes and Nectus fields.
SAML Access Groups: Click on the “+” button to add the SAML user groups from the SAML Server.
Members of the selected groups will be allowed to login to Nectus.
SAML Access Accounts: Click on the “+” button to add individual user accounts from the SAML Server.
Selected users will be allowed to login to Nectus.
How to Generate Direct Access URL for Graphs and Dashboards
Nectus DashboardsHow to Generate Direct Access URL for Graphs and Dashboards
Quick Start
Step 1: Login to the Nectus Portal, right-click on the specific device, and select the Graphs -> Availability Graph option.
Step 2: On the Availability Graph page, click on the Generate Direct Access URL button.
Step 3: Consequently, a unique URL is generated for this graph.
Nectus allows you to include additional configurations such as URL name, access control, link expiration date, etc.
Lastly, click on the Save And Copy button.
Step 4: Open the URL in the browser.
The graph page will automatically load.
Note: The same steps should be followed to generate other graphs like Latency, Lost Pings, Trace, etc.
Step 5: Likewise, Nectus also allows us to generate direct access URLs for the dashboards.
To create one, navigate to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Dashboards -> Low Level Dashboard.
Step 6: On the Low-level Dashboard model, click on the gear icon (settings option) in the top right corner.
Step 7: In the Settings model, click on the Generate Direct URL button.
Step 8: Subsequently, a unique URL is generated for this dashboard.
Once again, Nectus allows us to add additional configurations such as name, view access control using mandatory login, link expiry dates, etc.
Finally, click on the Save And Copy button.
Step 9: To share the copied URL with relevant users/teams, paste the URL in the browser. The dashboard page will then automatically load.
Note: The same steps should be followed for other dashboards like Network Monitoring, Server Monitoring, DB Monitoring, HTTP URL Monitoring, etc.
How to Create a Maintenance Events in Nectus
Nectus Installation, Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Create a Maintenance Events in Nectus
You can create maintenance events in Nectus to allow everybody to see that specific objects (Interface, Device or Site) have an active or scheduled maintenance.
During active maintenance events corresponding objects in Nectus are displayed with a blue status icon.
This article shows how to create a maintenance event for a Device.
Similar process can be used for creation of Interface or Site level maintenance events.
Step 1: Login to the Nectus Portal, Right click on the specific device and select the Properties option.
Step 2: Go to the Maintenance Events Tab and Click on Add button to create a new Maintenance Event
Step 3: Provide the suitable description and scheduling information.
Select the appropriate checkbox to disable monitoring or alerting during the activity time.
Step 4: We can also use the status, time range, objects type dropdown to filter the maintenance events to manage it.
Step 5. To See Complete list of all Maintenance events, go to Monitoring -> Global Monitoring Settings -> Maintenance Events.
How to Combine Multiple Interface Utilization Graphs Into One
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesStep 1: Login to the Nectus GUI, and go to the specific device, identify the interfaces which have to be graphed in a combined view.
Step 2: Select the multiple interfaces, Right-Click on the Selected Interfaces and go to Graphs -> Interface Utilization Graph.
Step 3: Here is the default view, where all utilization graphs are stacked vertically.
Step 4: Use superimpose option (Superimpose, Superimpose with Summary) which merges the selected multiple interface utilization graphs into a single graph.
Restricting Users From Using Specific Nectus GUI Features
Technical NotesRestricting Users From Using Specific Nectus GUI Features
Quick Start
Step 1: Let’s login to the Nectus GUI using the superadmin user credentials.
Step 2: Click on the Setting Menu and select admin accounts (Settings -> Admin Accounts).
Now the new modal opens with two tabs (Users List, User Groups).
Step 3: First, let’s create a new group by clicking the Create Button.
Provide the appropriate group name and select the features that need to be allowed or disabled for this user group.
Here, we are hiding Call Records, Network Discovery, Ping Plotter, and so on. Last, click on the OK button and create a new group.
Step 4: Now, let’s create a new user and add to newly created group.
Go to the User List tab in the Admin Account Modal and Click on Create User Button.
Complete the basic information and, under the Group dropdown option, select the appropriate group.
Step 5: Now, we can see the new user is added and mapped to appropriate group.
Step 6: Log-in with the newly created user credentials to validate the provided features restriction.
How to Override Group Based Monitoring Settings for Specific Devices
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Override Group Based Monitoring Settings for Specific Devices
By default, all the monitoring settings for each device are defined in the Monitoring Profile that is assigned to
Monitoring Group where this specific device is a member of.
Starting from 1.67.1 release Nectus adds ability to override group-based monitoring settings for each device.
Step1: Login to the Nectus Portal and go to the specific device on which you need to perform the monitoring settings override.
Right click on the device and select Properties.
Step 2: Select Metrics Tab in the properties modal and apply all the required overrides to the required metrics.
Check button “Local Override” must be selected for all the metrics that must have priority (override) over Group based monitoring settings.
Creating New Interface Monitoring Groups and Profiles
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesStep 1: Login to the Nectus Portal and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> SNMP Interfaces Monitoring Settings.
Step 2: Monitoring Profile Creation – Go to the SNMP Interface Monitoring Profile Tab by clicking the Add Profile button.
Name the profile, enable the relevant options, and click the OK button.
Now, we can see that the newly created profile is shown in the table.
Step 3: Monitoring Group Creation – Next, let’s go to the SNMP Interface Monitoring Groups tab and create a new interface monitoring group by clicking Add Group.
Step 4: Assigning Interfaces to Monitoring Group – Click on the interface group name to add the appropriate device interfaces information to the group.
We can also filter the interfaces based on operational status, admin status, site and device types and lastly click on Save button.
Step 5: Assigning Monitoring Profile to Monitoring Group – Enable the monitoring and select the previously created monitoring profile from the dropdown.
Step 6: Defining Alert Recipients for Monitoring Group – Now, let’s configure recipients for alerting by clicking the email button.
It allows us to add SMS and email recipients to a list. Further, we can also select the appropriate alert templates to send alert/sms.
Done.
Creating New Device Monitoring Groups and Profiles
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesNetwork device monitoring in Nectus is controlled by device monitoring groups and associated monitoring profiles.
There are two default monitoring groups: “Default Monitoring Group” and “No Monitoring Group”
By default all devices are automatically assigned to Default Monitoring Group where all basic monitoring metric are enabled.
“No Monitoring Group” is used as a parking place for devices that do not required monitoring.
In some cases additional monitoring groups may be required and this article explains the steps required to create additional monitoring groups.
Step 1: Login to the Nectus Portal and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> SNMP Devices Monitoring Settings.
Step 2: Monitoring Profile Creation – Go to the SNMP Device Monitoring Profile by clicking the Add Profile button. Name the profile, enable the relevant options, and click the OK button.
Now, we can see that the newly created profile is shown in the table.
Step 3: Monitoring Group Creation – Next, let’s go to the SNMP Device Monitoring Groups tab and create a new device monitoring group.
Step 4: Assigning Devices to Monitoring Group – Click on the device group name to add the appropriate device information to the group and lastly click on Save and Ok buttons.
Step 5: Assigning Monitoring Profile to Monitoring Group – Enable the monitoring and select the previously created monitoring profile from the dropdown.
Step 6: Defining Alert Recipients for Monitoring Group – Now, let’s configure recipients for alerting by clicking the email button. It allows us to add SMS and email recipients to a list.
Done.
Nectus SAML Integration
Nectus Installation, Technical NotesStep 1: Log in to the Nectus Portal and go to Settings > General Settings > SAML Integration.
Step 2: In the SAML Integration Modal, under the General tab, provide the Entity ID, SSO URL and SLO URL, Certificate, Organization URL and API token.
Refer to SAML provider documentation on how to generate Certificate and API key.
Step 3: Under Attribute Mappings, provide the SAML attributes for First Name, Last Name, Email and membership Groups.
This mapping is between SAML attributes and Nectus fields.
Step 4: Click on the “+” button to add the SAML user groups from the SAML Server.
Members of the selected groups will be allowed to login to Nectus.
Step 5: Click on the “+” button to add individual user accounts from the SAML Server.
Selected users will be allowed to login to Nectus.
Automating Selection of Interfaces Enabled for Monitoring
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesAutomating Selection of Interfaces Enabled for Monitoring
By default, Nectus does not monitor any Interfaces and you must select which interfaces you want to be monitored.
You can select Interfaces manually by adding it to one of the Interface monitoring groups or you can build auto-population rules
that will automatically select Interfaces based on predefined rules. Rules will be executed once a day (at 2:00AM)
Step 1: Login to the Nectus portal and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> SNMP Interfaces Monitoring Settings option.
Step 2: Go to the SNMP Interfaces Monitoring Groups tab and click on the Auto Population Rules under the Default Monitoring Group.
Step 3: Click on the Rule to add a new auto-population rule. Once a day, interfaces that conform to the defined rules
will be added to the corresponding monitoring group.
You can add individual rules or you can create group of rules with AND/OR logic.
How to Manually Add Device Classification for Unknown Devices
Nectus Installation, Network Discovery, Technical NotesHow to Manually Add Device Classification for Unknown Devices
Step 1:
Nectus maintains internal device classification database where each device is assigned a major platform category and a device model name.
Classification is associated with device SNMP Platform OID: (.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0)
Classification database is updated daily and support for new devices included in every Nectus update. But in some rare cases Nectus might not have classification info for specific device and this device will appear under “Unknow Category” in SNMP device tree.
Nectus GUI allows customer to manually add Unknown device classification information directly into Nectus server database.
Right-click on SNMP Platform ID value and select “Add Product Definition for x.x.x.x.x.x.x” from the SNMP Devices context menu.
Step 2: As the product definition modal opens, provide the sub-category (product) name, and select a category from the drop-down menu. If there is no applicable category name in the drop-down menu, you can define a new category name.
Controlling Nectus Database Size Growth with Data Retention Rules
Nectus Installation, Network Monitoring, Technical NotesControlling Nectus Database Size with Data Retention Rules
Step 1: Login to Nectus portal and go to Monitoring 🡪 Global Monitoring Settings option.
Step 2: Go to the “Data Retention” tab in the Monitoring Settings modal. It shows retention settings in days for each monitoring metric.
Further, it also shows the current database size and the data daily growth rate.
These two options give you a good idea of how to plan your retention period and storage requirements.
Step 3: Provide the retention period in days with maximum of 3650 days (10 years) and minimum of 1 day.
Step 4: We also have two key options such as Refresh and Cleanup.
Refresh – Will fetch updated size information from the server
Cleanup – Starts removal of monitoring data from the Nectus database according to retention settings.
Note: Normally Cleanup happens automatically every day at 2:00AM.
How to Control Logging in Nectus via .ini Files
Nectus Installation, Technical NotesHow to Control Logging in Nectus via .ini Files
If there is a need to reduce amount of disk space Nectus Logs take you can adjust logging verbosity or disable logging completely for each Nectus Service.
Logging settings for each service is controlled by .INI files located in C:\Program Files\Nectus\
Any changes to .INI files do require restart of the corresponding Nectus Service.
To adjust logging settings follow these steps
Step 1: Stop the required Nectus services on the server.
Step 2: Go to “C:\Program Files\Nectus” on the Nectus server.
Step 3: Update the logging configuration in corresponding .ini files located in “C:\Program Files\Nectus” as per the requirement and save them.
Step 4: Start all the Nectus services on the server.
Step 5: To check the current size of log folders, navigate to “C:\Program Files\Nectus\Logs.”
How to Monitor Number of Active TCP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Monitor Number of Active TCP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Quick Start
Step 1: Login to Nectus and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> Custom SNMP Trackers.
Step 2: Click on the Create button to create a new SNMP Custom Tracker that will be collecting number of active TCP sessions every 5min.
Palo Alto SNMP OID that returns number of active TCP sessions: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25461.2.1.2.3.4.0
Step 3: Enable the tracker, provide the tracker name, SNMP OID, unit name and data type.
Alerting option can be enable with predefined threshold value.
Step 4: If not created in advance, create the SNMP Device View by clicking the + (plus) button.
Provide the view name and select the Palo Alto Firewalls from available device list for monitoring.
Click “Ok” to finish tracker creation.
Step 5: For reporting, Go to the Reports -> “Top” reports -> Top Custom SNMP Trackers
Step 6: Select the appropriate report and tracker name to get the max. and min. values.
Click on the Graph button to get the tracker trend in visual form.
Done.
How to Monitor Number of Active UDP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Monitor Number of Active UDP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Quick Start
Step 1: Login to Nectus and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> Custom SNMP Trackers.
Step 2: Click on the Create button to create a new SNMP Custom Tracker that will be collecting number of active UDP sessions every 5min.
Palo Alto SNMP OID that returns number of active UDP sessions: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25461.2.1.2.3.5.0
Step 3: Enable the tracker, provide the tracker name, SNMP OID, unit name and data type.
Alerting option can be enable with predefined threshold value.
Step 4: If not created in advance, create the SNMP Device View by clicking the + (plus) button.
Provide the view name and select the Palo Alto Firewalls from available device list for monitoring.
Click “Ok” to finish tracker creation.
Step 5: For reporting, Go to the Reports -> “Top” reports -> Top Custom SNMP Trackers
Step 6: Select the appropriate report and tracker name to get the max. and min. values.
Click on the Graph button to get the tracker trend in visual form.
Done.
How to Monitor Number of Active ICMP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Monitor Number of Active ICMP Sessions on PaloAlto Firewalls
Quick Start
Step 1: Login to Nectus and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> Custom SNMP Trackers.
Step 2: Click on the Create button to create a new SNMP Custom Tracker that will be collecting number of active ICMP sessions every 5min.
Palo Alto SNMP OID that returns number of active ICMP sessions: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25461.2.1.2.3.6.0
Step 3: Enable the tracker, provide the tracker name, SNMP OID, unit name and data type.
Alerting option can be enable with predefined threshold value.
Step 4: If not created in advance, create the SNMP Device View by clicking the + (plus) button. Provide the view name and select the Palo Alto Firewalls from available device list for monitoring.
Click “Ok” to finish tracker creation.
Step 5: For reporting, Go to the Reports -> “Top” reports -> Top Custom SNMP Trackers
Step 6: Select the appropriate report and tracker name to get the max. and min. values. Click on the Graph button to get the tracker trend in visual form.
Done.
How to Monitor Number of Palo Alto VPN (Global Protect) Users
Network Monitoring, Technical NotesHow to Monitor Number of Palo Alto VPN (Global Protect) Users
Step 1: Login to Nectus and go to Monitoring -> Network Monitoring Settings -> Custom SNMP Trackers.
Step 2: Click on the Create button to create a new SNMP Custom Tracker that will be collecting number of connected VPN users every 5min.
Palo Alto SNMP OID that returns number of connected users: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25461.2.1.2.5.1.3.0
Step 3: Enable the tracker, provide the tracker name, SNMP OID, unit name and data type.
Alerting option can be enabled with predefined threshold values.
Step 4: If not created in advance, create the SNMP Device View by clicking the + (plus) button.
Provide the view name and select the Palo Alto Firewalls from available device list for monitoring.
Click “Ok” to finish tracker creation.
Step 5: For reporting, Go to the Reports -> “Top” reports -> Top Custom SNMP Trackers
Step 6: Select the appropriate report and tracker name to get the max. and min. values.
Click on the Graph button to get the tracker trend in visual form.
Done.
Nectus DB Migration by manually copying DB files to a new server.
Nectus Installation, Technical NotesNectus DB Migration by manually copying DB to a new server.
Step 1: Prepare new server by performing clean Nectus installation with the same Nectus version as on old server
Step 2: Stop all Nectus services on the new server
Step 3: Delete all the content from “C:\Program Files\Nectus\Database” folder on new server.
Step 4: Copy complete “C:\Program Files\Nectus\Database” folder from the old Nectus server to the “C:\Program Files\Nectus\Database” folder on the new server
Step 5: Copy file “C:\Program Files\Nectus\Web\Apache24\htdocs\protected\config\database.ini” from old server to the same location on new server.
(Overwrite existing file).
Step 6: In all *.ini files located in “C:\Program Files\Nectus” folder on new server update
DatabasePassword=wL1Kdnl6h$ line with a new password for username “vconsole” which can be found in
“C:\Program Files\Nectus\Web\Apache24\htdocs\protected\config\database.ini” file.
Step 7: Open the Registry Editor and in “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE -> SOFTWARE -> Virtual Console LLC -> Nectus”
update passwords for the three database accounts. (New passwords can be found in database.ini file)
Step 8: Start all Nectus Services
Migration Complete.
Performing Nectus DB migration to a new server with “DB Migration” tool
Nectus Installation, Technical NotesPerforming Nectus DB migration to a new server with “DB Migration” tool
DB Migration tool is only available to users with Super Admin rights.
Prepare new server with clean Nectus installation with the same Nectus version as on old server.
Step 1: Login to the old Nectus server and go to Settings -> Database -> DB Migration.
Step 2: In the DB Migration window specify IP address of the new server and password for “vconsole” DB account from the new server.
Note: Password for “vconsole” account can be found in the
“C:\Program Files\Nectus\Web\Apache24\htdocs\protected\config\database.ini” file on the new server.
Step 3: Click on the Test Connection. It will perform the credentials and Nectus version checks.
Step 4: Start migration by clicking on “Start DB migration”.
Depending on the database size migration may take several hours.